Heat illness is a serious concern, especially during hot weather. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or fitness level. That’s why it’s important to have a heat illness prevention program in place to help protect your employees, customers, and visitors.
A heat illness prevention program should include a variety of elements, such as:
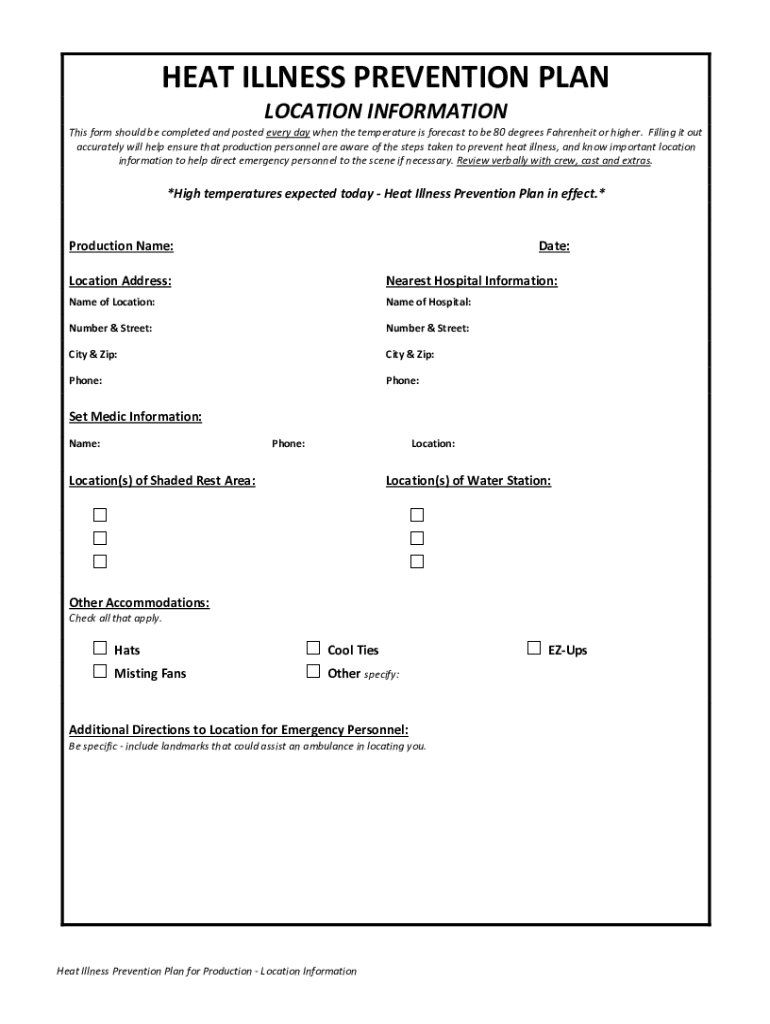
What to Include in a Heat Illness Prevention Program
A heat illness prevention program should include the following:
- Education and training: Employees should be educated about the signs and symptoms of heat illness, as well as how to prevent it. This can be done through training sessions, posters, or online resources.
- Engineering controls: Engineering controls can be used to reduce the risk of heat illness. These controls can include air conditioning, fans, and shade. Employers should also consider the design of their workplace to minimize heat exposure.
- Work practices: Work practices can also be used to reduce the risk of heat illness. These practices can include scheduling work during cooler hours, providing rest breaks, and encouraging employees to drink plenty of fluids.
- Personal protective equipment: Personal protective equipment (PPE) can be used to protect employees from heat exposure. This PPE can include hats, sunglasses, and sunscreen.
Steps to Develop a Heat Illness Prevention Program
To develop a heat illness prevention program, employers should follow these steps:
- Identify hazards: The first step is to identify the hazards that could lead to heat illness. Employers should consider the type of work being done, the climate, and the time of year.
- Assess risks: Once the hazards have been identified, employers need to assess the risks of heat illness. This assessment should include the likelihood of heat illness occurring and the severity of the potential consequences.
- Develop controls: Once the risks have been assessed, employers need to develop controls to reduce the risk of heat illness. These controls can include the use of engineering controls, work practices, and PPE.
- Implement controls: Once the controls have been developed, employers need to implement them. This includes training employees on the controls and providing them with the necessary resources.
- Evaluate effectiveness: Finally, employers need to evaluate the effectiveness of their heat illness prevention program. This evaluation should include monitoring the number of heat illness cases and making adjustments to the program as needed.
By following these steps, employers can develop and implement a heat illness prevention program that will help protect their employees from this serious health hazard.
Heat illness is a preventable condition. By taking the necessary precautions, you can help protect yourself and others from this serious health risk.



