Utilizing such a structured approach offers several advantages. It promotes efficient problem resolution by ensuring all relevant information is captured and communicated effectively. This minimizes ambiguity and fosters a shared understanding between the organization and its suppliers. Furthermore, documented corrective actions create a valuable record for tracking performance, identifying trends, and driving continuous improvement throughout the supply chain. This ultimately leads to enhanced product quality, reduced risk, and stronger supplier relationships.
This article will further explore the key components of these crucial documents, provide practical guidance on their implementation, and discuss best practices for maximizing their effectiveness in various supply chain scenarios.
Key Components of a Supplier Corrective Action Request
Effective corrective action requests require specific information to ensure clarity and facilitate resolution. The following components are crucial for a comprehensive and actionable document.
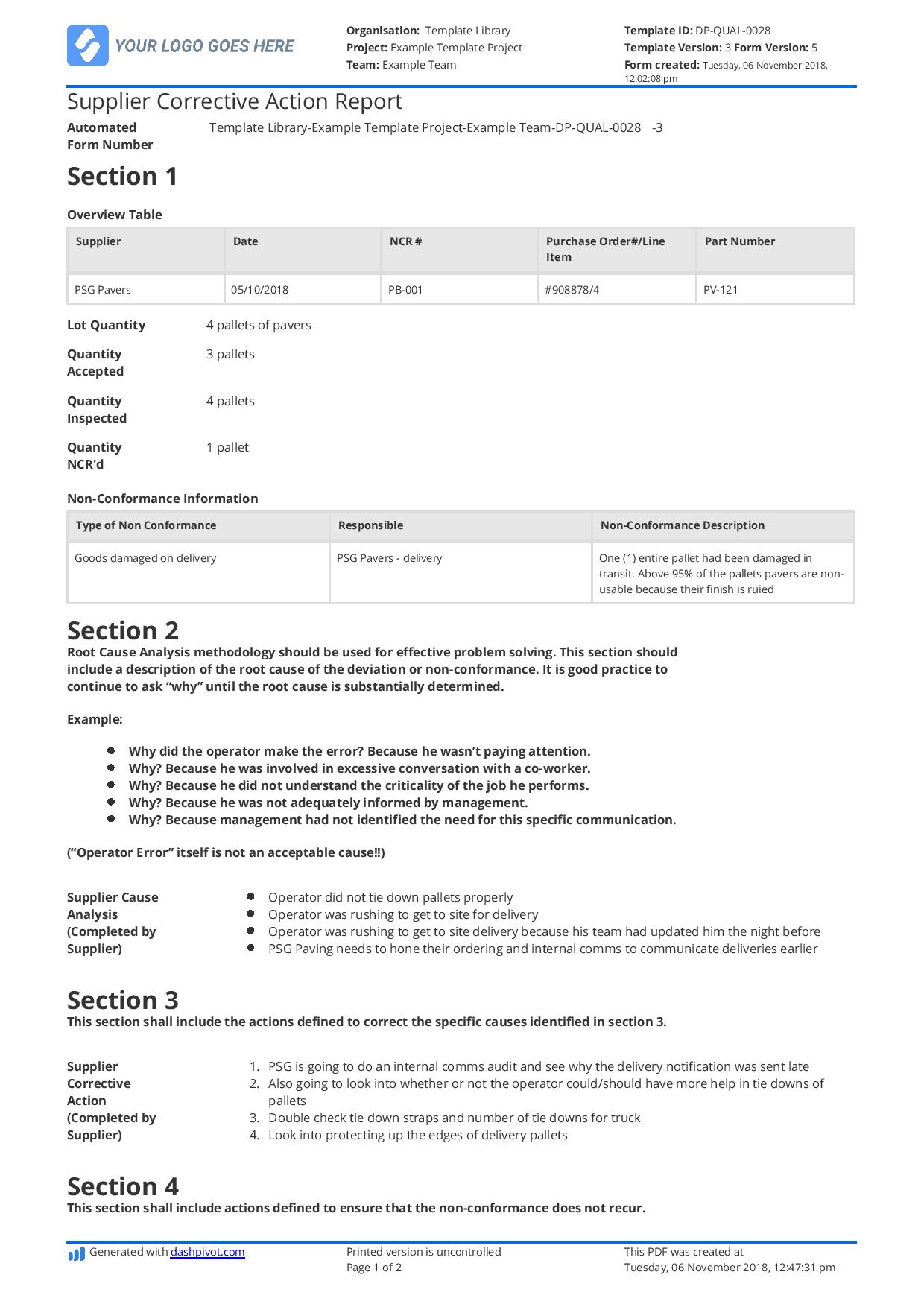
1: Identification Information: This section clearly identifies the requesting organization, the supplier involved, and relevant contact information for both parties. It should also include unique identifiers such as request date and a reference number for efficient tracking and retrieval.
2: Description of the Nonconformance: A precise and detailed description of the issue is essential. This should include the nature of the problem, the specific requirements not met, and the potential impact of the nonconformance.
3: Objective Evidence: Supporting documentation, such as inspection reports, test results, or photographs, should be included to substantiate the reported issue and provide clear evidence of the nonconformance.
4: Required Corrective Action: This section specifies the actions the supplier must take to address the root cause of the problem and prevent recurrence. Clear expectations and measurable targets should be defined.
5: Root Cause Analysis: The supplier should be required to conduct a thorough root cause analysis to identify the underlying cause of the nonconformance. This analysis should be documented and submitted as part of the response.
6: Implementation Timeline: A realistic timeframe for implementing the corrective actions should be established and agreed upon by both parties. This ensures timely resolution and prevents further delays.
7: Verification of Effectiveness: A method for verifying the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions should be defined. This may involve follow-up inspections, testing, or data analysis.
8: Preventative Actions: The supplier should outline preventative measures to be implemented to avoid similar issues in the future. These actions should address systemic weaknesses and improve overall processes.
Accurate documentation and a structured approach are critical for successful supplier corrective actions. These elements enable effective communication, facilitate timely resolution, and promote continuous improvement within the supply chain.
How to Create a Supplier Corrective Action Request Template
Creating a standardized template ensures consistency and efficiency in addressing supplier performance issues. A well-structured template facilitates clear communication and promotes timely resolution of quality discrepancies.
1: Define Scope and Applicability: Clearly define the scope of the template, specifying the types of nonconformances it covers and the relevant industry or regulatory requirements.
2: Incorporate Header Information: Include fields for essential identification details, such as the organization’s name and contact information, the supplier’s details, and unique identifiers like a request date and reference number.
3: Structure the Nonconformance Description Section: Provide clear instructions and fields for describing the nonconformance in detail. Include prompts for specifying the nature of the issue, impacted requirements, and potential consequences.
4: Incorporate Evidence Collection Fields: Designate areas for attaching objective evidence, such as inspection reports, test results, or photographs. Specify acceptable file formats and size limits.
5: Outline Corrective Action Requirements: Provide sections for outlining required corrective actions, specifying expected outcomes and measurable targets. Include fields for root cause analysis documentation.
6: Establish Timeline Expectations: Include fields for defining implementation timelines and deadlines for corrective actions. Provide clear instructions for communicating progress updates.
7: Define Verification Procedures: Specify the methods and criteria for verifying the effectiveness of the corrective actions. Include fields for documenting verification results.
8: Incorporate Preventative Action Planning: Include sections for outlining preventative actions to avoid recurrence. Encourage proactive identification of systemic weaknesses and process improvements.
A well-designed template streamlines the corrective action process, ensuring consistent documentation, promoting efficient communication, and driving continuous improvement in supplier performance.
Standardized documentation for addressing supplier quality issues provides a structured framework for ensuring product quality, minimizing risks, and fostering stronger supplier relationships. Through clear communication of nonconformances, required corrective actions, and preventative measures, these documents drive continuous improvement throughout the supply chain. Effective implementation relies on comprehensive templates encompassing clear identification information, detailed problem descriptions, objective evidence, root cause analysis, timelines, and verification procedures.
Ultimately, the consistent application of these structured approaches leads to enhanced supply chain performance, reduced costs associated with quality issues, and improved overall product reliability. Organizations prioritizing proactive quality management and robust supplier relationships recognize the value of these tools in mitigating risk and achieving long-term success.