Utilizing such a structured approach improves communication among stakeholders, reduces errors and delays, and enhances overall product quality. It provides a traceable record of modifications, supporting better version control and simplifying auditing processes. A well-defined process for implementing modifications minimizes risks associated with uncontrolled changes and ensures consistent application of engineering best practices.
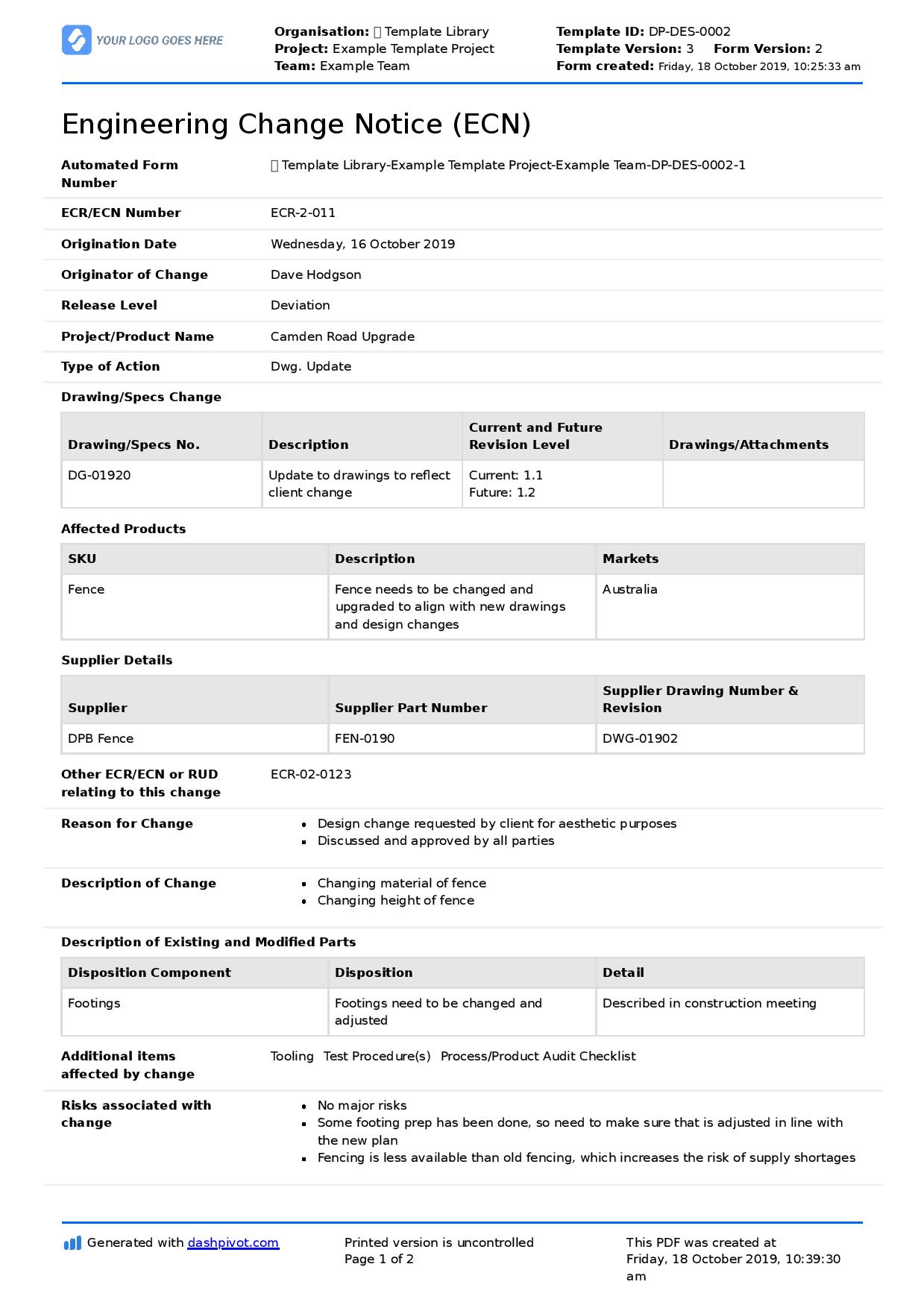
The subsequent sections delve into the core components of these forms, best practices for their utilization, and practical examples demonstrating their efficacy in various engineering disciplines.
Key Components of an Engineering Change Request
Effective management of modifications relies on comprehensive documentation. Several key components ensure clarity, traceability, and efficient processing.
1. Identification/Tracking Number: A unique identifier allows for easy tracking and retrieval of the request throughout its lifecycle.
2. Requestor Information: Details regarding the individual or team initiating the modification, enabling clear communication and accountability.
3. Date of Request: Timestamping the request provides context and aids in tracking timelines.
4. Description of Change: A clear and concise explanation of the proposed modification, detailing the specific alteration and its intended effects.
5. Justification/Rationale: Explanation of the reasons necessitating the change, including the problem being addressed or the improvement sought.
6. Impact Assessment: Analysis of potential effects on related components, systems, or processes, including cost, schedule, and performance considerations.
7. Affected Documents/Items: List of specific documents, drawings, or other items requiring updates as a result of the implemented modification.
8. Approval Signatures: Designated spaces for relevant stakeholders to formally approve or reject the proposed change.
Accurate and complete information within each component ensures efficient evaluation, approval, and implementation, minimizing potential risks and maximizing positive outcomes.
How to Create an Engineering Change Request Template
Developing a standardized template ensures consistency and efficiency in managing engineering modifications. A well-structured template facilitates clear communication, simplifies tracking, and reduces errors.
1: Define Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the types of changes the template will encompass and the intended users. Consider the specific needs of the organization and the complexity of products or processes involved.
2: Determine Required Information: Identify essential information needed to evaluate and process change requests, including identification details, requestor information, description of the change, justification, impact assessment, and affected items.
3: Design the Layout: Create a clear and logical layout for the template, using headings, subheadings, and tables to organize information. Ensure adequate space for all required fields and consider incorporating checklists or drop-down menus for standardized data entry.
4: Establish an Approval Workflow: Define the approval process, including designated approvers for different types of changes. Incorporate spaces for signatures and dates to document approvals and maintain traceability.
5: Implement Version Control: Include a mechanism for version control to track revisions and maintain a history of changes to the template itself.
6: Train Users: Provide training to all users on how to complete and submit change requests using the template. Clear instructions and practical examples promote consistent application and accurate data capture.
7: Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review the template’s effectiveness and make necessary updates based on user feedback and evolving organizational needs. This ensures the template remains relevant and continues to support efficient change management.
A robust template, coupled with comprehensive user training and regular review, forms the cornerstone of a successful engineering change management process. This standardized approach contributes significantly to product quality, reduced development time, and overall project success.
Standardized forms for requesting engineering changes provide a crucial framework for managing modifications throughout a product’s lifecycle. From initial design through manufacturing and post-production, these structured documents facilitate clear communication, ensure traceability, and minimize the risks associated with design alterations. Key components such as unique identifiers, detailed descriptions of changes, impact assessments, and approval workflows contribute to a robust change management process. Proper template development, coupled with user training and regular review, further enhances the efficacy of these tools.
Effective management of engineering changes is essential for maintaining product quality, controlling costs, and adhering to project schedules. Adopting a systematic approach, facilitated by well-designed templates and established procedures, is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize product development and achieve long-term success in competitive markets.